- You have no items in your shopping cart
- Continue Shopping

Welcome to the fascinating realm of cannabinoids! Derived from the Cannabis plant, these compounds have garnered immense interest for their diverse properties and potential benefits. Let’s delve into this intricate world, unraveling the science behind cannabinoids and their effects on the human body.
Understanding Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids, with over 480 variants identified, are pivotal components of the Cannabis plant. Among these, Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD) stand out as the most prominent. However, the spectrum extends further to encompass eight major cannabinoid acids, including CBGA, THCA, and CBDA, each playing a unique role in the plant’s biology.
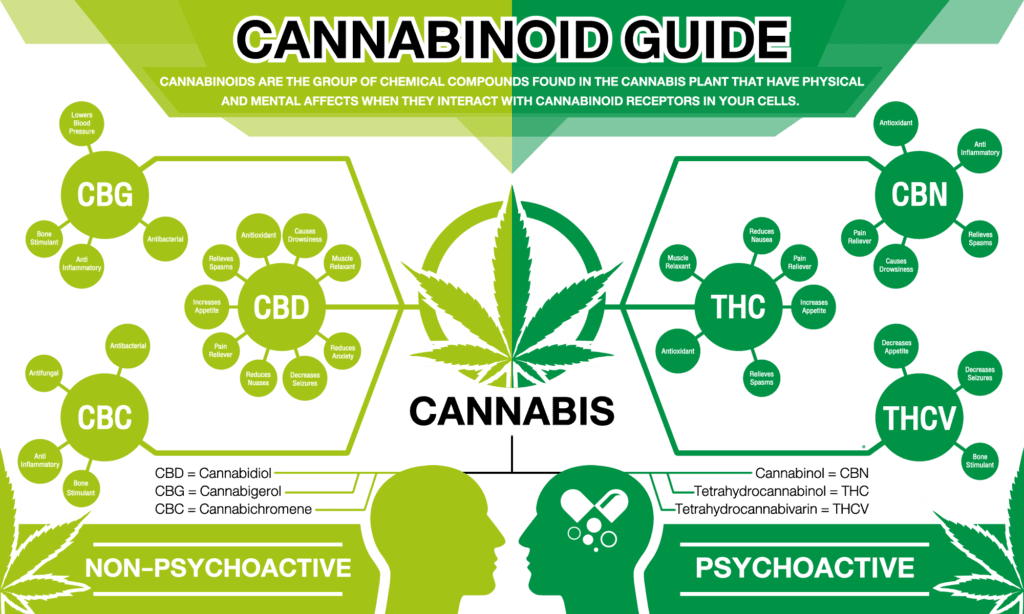
Conversion and Composition
In the realm of cannabis science, there exists a captivating process known as decarboxylation, which plays a pivotal role in transforming cannabinoid acids into their potent, neutral counterparts. This metamorphosis is not merely a chemical reaction; it’s a gateway to unlocking the therapeutic potential and diverse applications of cannabinoids like CBG, THC, and CBD.
Picture this: cannabinoid acids, the precursors to the well-known cannabinoids, exist in their natural state within the cannabis plant. However, it’s through the application of heat that these acids undergo a remarkable conversion, shedding their acidic nature and emerging as the neutral cannabinoids that hold immense promise in the realm of health and wellness.
Deciphering Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation, while sounding complex, is essentially the process by which cannabinoids lose a carboxyl group (-COOH) through exposure to heat, triggering a cascade of chemical reactions that fundamentally alter their properties. This transformation is particularly significant as it not only enhances the potency of cannabinoids but also broadens their spectrum of potential applications.
For instance, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), the non-intoxicating precursor to THC, becomes the psychoactive compound THC upon decarboxylation. This conversion is what activates the intoxicating effects commonly associated with cannabis consumption. Similarly, cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) transforms into the widely celebrated compound CBD, known for its myriad therapeutic properties ranging from pain relief to anxiety management.
Applications of Decarboxylation
Understanding the intricacies of decarboxylation is crucial for harnessing the full potential of cannabinoids in various fields, including medicine, wellness, and even culinary arts. By applying precise heat and time parameters, researchers and enthusiasts alike can tailor the composition of cannabinoids to suit specific needs, whether it’s crafting potent therapeutic formulations or creating delectable edibles with precise cannabinoid profiles.
In essence, decarboxylation is not merely a scientific process; it’s a gateway to unlocking the transformative power of cannabinoids. Through this meticulous conversion, cannabinoid acids evolve into versatile compounds with a myriad of applications, revolutionizing the landscape of cannabis research, industry, and consumer products. So, the next time you indulge in a CBD-infused treat or explore the therapeutic benefits of cannabis, remember the intriguing journey these cannabinoids underwent through the remarkable process of decarboxylation.
Effects and Receptor Interaction
The effects of cannabinoids are intricately linked to their interaction with specific cannabinoid receptors, primarily CB1 and CB2, distributed throughout the central nervous system. While THC is renowned for its psychoactive effects, other cannabinoids like CBD offer a plethora of therapeutic benefits without inducing intoxication. Moreover, lesser-known compounds like THCV exhibit nuanced effects, influencing the overall impact of cannabis products.
Exploring Synergies
One of the most intriguing aspects of cannabinoids is their synergistic effects. CBD, for instance, modulates the interaction between THC and CB1 receptors, altering the overall experience. Similarly, THCV demonstrates dose-dependent effects, highlighting the importance of dosage in cannabinoid consumption.
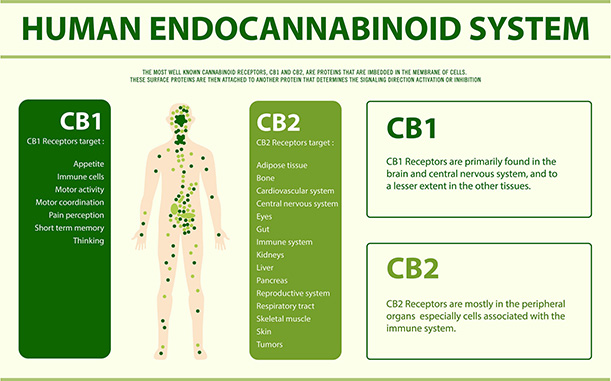
Implications for Research and Application
Despite the growing interest in cannabinoids, there is still much to explore, especially regarding lesser-known compounds and their potential therapeutic applications. By understanding the intricate interplay between cannabinoids and the human body, we can unlock new avenues for medical research and personalized healthcare.
Conclusion
Cannabinoids represent a vast and complex domain with immense potential for scientific exploration and therapeutic innovation. As we continue to unravel their mysteries, let us embrace a nuanced understanding of these compounds and their diverse effects on human physiology. From enhancing well-being to treating medical conditions, cannabinoids offer a promising frontier for future research and application.
